E-COMMERCE: DIGITAL MARKET, DIGITAL GOODS
WHY E-COMMERCE IS DIFFERENT
Internet and e-commerce
technologies are much more rich and powerful than previous technology
revolutions like radio, television, and the telephone.
8 Unique features of Internet and Web as commercial
- Ubiquity
Effect:
- Marketplace removed from temporal, geographic locations to become "marketspace"
- Enhanced customer convenienceand reduced shopping costs
- Global Reach
Effect:
- Commerce is enabled across cultural and national boundaries seamlessly and without modification.
- The marketspace includes, potentially, billions of consumers and millions of businesses worldwide.
- Universal Standarts
Effect:
- Disparate computer systems can easily communicate with each other.
- Lower market entry costs—costs merchants must pay to bring goods to market
- Lower consumers’ search costs—effort required to find suitable products
- Interactivity
Effect:
- Consumers engaged in dialog that dynamically adjusts experience to the individual
- Consumer becomes co-participant in process of delivering goods to market.
- Richness
Video, audio, and text messages are
possible.
Effect:
Effect:
- Possible to deliver rich messages with text, audio, and video simultaneously to large numbers of people.
- Video, audio, and text marketing messages can be integrated into single marketing message and consumer experience.
- Information Density
The technology reduces
information costs and raises quality.
Effect:
Effect:
- Greater price transparency
- Greater cost transparency
- Enables merchants to engage in price discrimination
- Personalization / Costumization
Effect:
- Personalization of marketing messages and customization of products and services are based on individual characteristics.
- Social Technology
The technology supports content
generation and social networking.
Effect:
Effect:
- New Internet social and business models enable user content creation and distribution, and support social networks.
- Many-to-many model
KEY CONCEPTS IN E-COMMERCE: DIGITAL MARKETS AND DIGITAL GOODS IN A GLOBAL MARKETPLACE
- Digital Market
Digital markets are very flexible and efficient because they operate with reduced search and transaction costs, lower menu costs (merchants’ costs of changing prices), greater price discrimination, and the ability to change prices dynamically based on market conditions.
- Digital Goods
Digital goods are goods that can be delivered over a digital network.
TYPES OF E-COMMERCE
The three major electronic commerce
- Business-to-consumer (B2C) e-commerce
Electronic commerce involves retailing
products and services to individual shoppers.
Example: BarnesandNoble.com
- Business-to-business
(B2B) e-commerce
Electronic commerce involves sales of goods
and services among businesses.
Example: ChemConnect’s
- Consumer-to-consumer (C2C) e-commerce
Electronic commerce involves consumers
selling directly to consumers.
Example: eBay
INTERNET BUSINESS MODEL
E-COMMERCE REVENUE MODELS
- Advertising Revenue Model
A Web site generates revenue by
attracting a large audience of visitors who can then be exposed to advertisements.
- Sales Revenue Model
Companies derive revenue by selling goods,
information, or services to customers.
- Subscription Revenue Model
A Web site offering content or services
charges a subscription fee for access to some or all of its offerings on an ongoing basis.
- Free / Freemium Revenue Model
Firms offer basic services or content
for free, while charging a premium for advanced or special features.
- Transaction Fee Revenue Model
A company receives a fee for enabling
or executing a transaction.
- Affiliate Revenue Model
Web sites (called “affiliate Web sites”) send
visitors to other Web sites in return for a referral fee or percentage of the revenue
from any resulting sales.
B2B E-COMMERCE: NEW EFFICIENCIES AND RELATIONSHIPS
Procurement requires significant
overhead costs, which Internet and networking helps automate.
Variety of different Internet-enabled technologies used in B2B
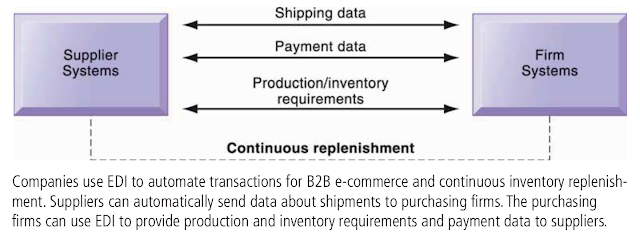
- Electronic data interchange (EDI)
Electronic data interchange enables the computer to computer exchange between two organizations of standard transactions such as
invoices, bills of lading, shipment schedules, or purchase orders. For example, procurement involves not only purchasing
goods and materials but also sourcing, negotiating with suppliers, paying for
goods, and making delivery arrangements.
- Private industrial networks (private
exchanges)
Private industrial networks typically consist of a large firm using a secure
Web site to link to its suppliers and other key business partners. Another term for
a private industrial network is a private exchange. An example is VW Group Supply, which links the Volkswagen Group and
its suppliers.
- Net marketplaces
Net marketplaces, which are sometimes called e-hubs, provide a single,
digital marketplace based on Internet technology for many different buyers and
sellers. Net marketplaces sell direct goods and some sell indirect goods. Direct goods are goods used in a production process, such as sheet steel for auto body production. Indirect goods are all other goods not directly involved in the production process, such as office supplies or products for maintenance and repair.
- Exchanges
Exchanges are independently owned third-party Net marketplaces that
connect thousands of suppliers and buyers for spot purchasing. For example,
Go2Paper enables a spot market for paper, board, and kraft among buyers and
sellers in the paper industries from over 75 countries.
THE MOBILE DIGITAL PLATFORM AND MOBILE
E-COMMERCE
M-commerce
- In 2012 is 10% of all e-commerce
- Fastest growing form of e-commerce, with some
areas expanding at a rate of 50 percent or more per year
- There were an estimated
4 billion cell phone users worldwide
- The main areas of growth in mobile e-commerce are retail sales at the top
Mobile 400 companies (Amazon and eBay), sales of digital content (music, TV shows and movies), local search
for restaurants, museums, stores.
Digital goods are goods that can be delivered over a digital network.
TYPES OF E-COMMERCE
The three major electronic commerce
- Business-to-consumer (B2C) e-commerce
Electronic commerce involves retailing
products and services to individual shoppers.
Example: BarnesandNoble.com
- Business-to-business (B2B) e-commerce
Electronic commerce involves sales of goods
and services among businesses.
Example: ChemConnect’s
- Consumer-to-consumer (C2C) e-commerce
Electronic commerce involves consumers
selling directly to consumers.
Example: eBay
INTERNET BUSINESS MODEL
E-COMMERCE REVENUE MODELS
- Advertising Revenue Model
A Web site generates revenue by
attracting a large audience of visitors who can then be exposed to advertisements.
- Sales Revenue Model
- Subscription Revenue Model
A Web site offering content or services
charges a subscription fee for access to some or all of its offerings on an ongoing basis.
- Free / Freemium Revenue Model
Firms offer basic services or content
for free, while charging a premium for advanced or special features.
- Transaction Fee Revenue Model
A company receives a fee for enabling
or executing a transaction.
- Affiliate Revenue Model
Web sites (called “affiliate Web sites”) send
visitors to other Web sites in return for a referral fee or percentage of the revenue
from any resulting sales.
B2B E-COMMERCE: NEW EFFICIENCIES AND RELATIONSHIPS
Procurement requires significant overhead costs, which Internet and networking helps automate.
Variety of different Internet-enabled technologies used in B2B
- Electronic data interchange (EDI)
- Private industrial networks (private exchanges)
- Net marketplaces
- Exchanges
THE MOBILE DIGITAL PLATFORM AND MOBILE E-COMMERCE
M-commerce
- In 2012 is 10% of all e-commerce
- Fastest growing form of e-commerce, with some areas expanding at a rate of 50 percent or more per year
- There were an estimated 4 billion cell phone users worldwide
- The main areas of growth in mobile e-commerce are retail sales at the top Mobile 400 companies (Amazon and eBay), sales of digital content (music, TV shows and movies), local search for restaurants, museums, stores.
LOCATION-BASED SERVICES AND APPLICATIONS
Location-based services
- Geosocial services
Can tell you where your friends
are meeting.
- Geoadvertising
Can tell you where to find the nearest
Italian restaurant
- Geoinformation services
Can tell you the price of a
house you are looking at, or about special exhibits at a museum you are passing.
OTHER MOBILE COMMERCE SERVICES
- Banks and credit card companies are rolling out services that let customers
manage their accounts from their mobile devices.
- Mobile display advertising are Apple’s iAd platform and Google’s AdMob
platform
- Games and entertainment, smartphones like the iPhone and Android-based devices offer downloadable
and streaming digital games, movies, TV shows, music, and ring tones.
BUILDING AN E-COMMERCE WEBSITE
Pieces of the Site-Building Puzzle
Assembling a team with the skills
required to make decisions about:
- Technology
- Site design
- Social and information policies
- Hardware, software, and
telecommunications infrastructure
Customer’s demands should drive the site’s technology and
design
Location-based services
- Geosocial services
- Geoadvertising
Can tell you where to find the nearest
Italian restaurant
- Geoinformation services
Can tell you the price of a
house you are looking at, or about special exhibits at a museum you are passing.
OTHER MOBILE COMMERCE SERVICES
- Banks and credit card companies are rolling out services that let customers manage their accounts from their mobile devices.
- Mobile display advertising are Apple’s iAd platform and Google’s AdMob platform
- Games and entertainment, smartphones like the iPhone and Android-based devices offer downloadable and streaming digital games, movies, TV shows, music, and ring tones.
BUILDING AN E-COMMERCE WEBSITE






This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDelete